Dr. Richard Desnoes, Dermatologist.
Eczema (Dermatitis) is an inflammatory condition affecting the outer layer of the skin. It may result from an individual’s genetic factors or as a consequence of the skin becoming sensitized or irritated by external chemical or physical agents (Contact Dermatitis).
Eczema may affect individuals of all ages including the young and elderly. Patients may experience itching which may be severe and interfere with quality of life and sleep. Affected skin may appear rough, reddish, bumpy, dry, and scaly. If the affected skin becomes infected with bacteria, it may become warm, swollen and drain clear fluid or pus. If the eczema becomes long standing or chronic, the skin may become thickened and leathery with changes in the colour of the affected areas.
The treatment for eczema involves the use of topical anti-inflammatory agents (steroids and non-steroidal agents), moisturizers, topical or oral antibiotics, oral antihistamines and avoiding contact with known triggers such as household cleaning agents and bleach. In many cases, the treatment for eczema does not provide a cure; however, you can get significant relief from the symptoms. See your doctor or dermatologist for further advice and treatment.
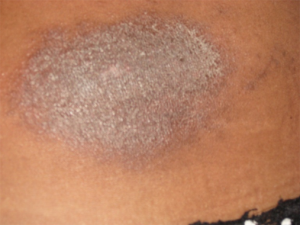
Dry, scaly, itchy patch on abdomen of patient with Contact Dermatitis.
